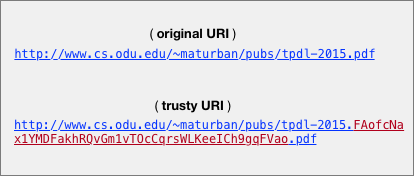
2017-12-11: Difficulties in timestamping archived web pages

Figure 1: A web page from nasa.gov is archived by Michael's Evil Wayback in July 2017. Figure 2: When visiting the same archived page in October 2017, we found that the content of the page has been tampered with. The 2016 Survey of Web Archiving in the United States shows an increasing trend of using public and private web archives in addition to the Internet Archive (IA). Because of this tendency we should consider the question of validity of archived web pages deleivered by these archives. Let us look at an example where the important web page https://climate.nasa.gov/vital-signs/carbon-dioxide/ , that keeps a record of the carbon dioxide (CO2) level in the Earth’s atmosphere, is captured by a private web archive “Michael’s Evil Wayback” on July 17, 2017 at 18:51 GMT. At this time, as Figure 1 shows, the CO2 was 406.31 ppm. When revisiting the same archived page in October 2017, we should be presented with the same content. Surpris...